What you need to know about bed bugs (and natural ways to get rid of them)
10/25/2018 / By Zoey Sky

According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), bed bugs are a public health hazard. Thankfully, these nasty pests don’t transmit diseases, unlike mosquitoes that spread malaria.
However, bed bugs need to be eliminated because exposure to these parasites may cause allergic reactions. In rare cases, some individuals bitten by bed bugs may suffer from anaphylactic shock. Scratching bed bug bites can also cause skin infections like impetigo.
Bed bug bites may cause lymphangitis, which occurs when bacteria or viruses invade the vessels of the lymphatic system via an infected cut or wound. The symptoms of lymphangitis include chills, fever, and a general sense of illness.
Bed bugs can even affect your mental health. Patients who have been bitten by the parasites report that they suffer from anxiety and insomnia, which affects their overall well-being.
The common bed bug and side effects of bites
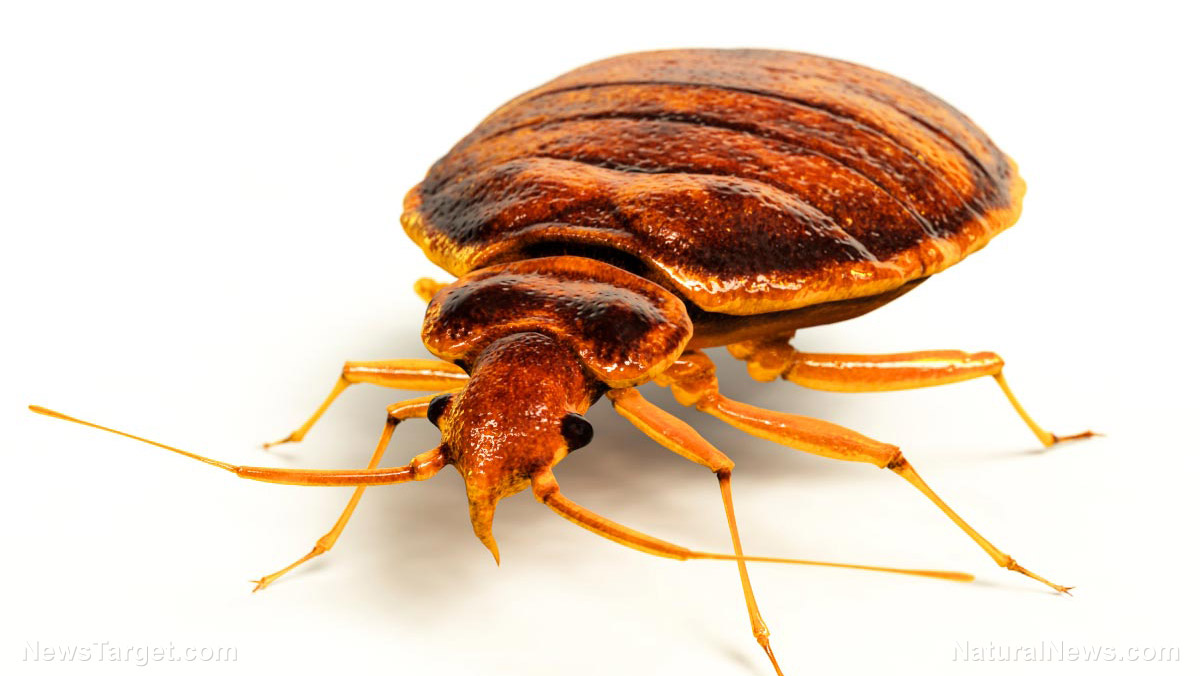
The common bed bug (Cimex lectularius) is a small, wingless insect. Unlike lice, bed bugs will bite any living creatures. Cimex hemipterus, a bed bug that can be found in tropical regions, will also infest bats and poultry.
Adult bed bugs are light to medium brown in color with flat, oval bodies that are about four millimeters long. They can increase in size once they have fed.
Newly hatched bed bugs, or “nymphs,” have a lighter color and they’re almost translucent. There are several nymph stages before adulthood. Before nymphs can turn into full-grown adult bed bugs, they must have a meal of blood. (Related: Cleanliness can prevent bugs as well as germs: Bed bugs love dirty laundry, study finds.)
Bed bugs can infest your home through several ways, like:
- Being brought in from other infested buildings via a visitor’s clothing or luggage.
- Through infested items like furniture.
- Transferred from bus or airline seats.
- Via ductwork or other passageways.
They can’t live on animals like dogs, but your pets are still susceptible to bed bug bites.
It can be difficult to locate bed bug nests, especially since they prefer to hide in luggage or in furniture. Use a magnifying glass to check every nook and cranny of your house. You can find bed bug nests by following trails of brown fecal markings or tiny drops of dried blood.
Possible bed bug hiding places include:
- Furniture
- Seams in backpacks, linens, and mattress
- The wooden parts of headboards and baseboards
Bed bugs are usually active at night and they will bite the exposed skin of sleeping humans to feed on their blood. Once they’re done feeding, the pests will return to their hiding places in mattress seams or other areas in your home.
Bites from these parasites are often painless, but they may cause itchy and raised welts on your skin. Bites from bed bugs are often confused with mosquitoes or fleas. However, while most flea bites appear around your ankles, bed bugs will bite any area of skin that’s exposed at night. Flea bites also tend to have a tell-tale central red spot.
A bed bug’s bite can also look like a mosquito bite, but the former will often bite a person multiple times in a straight line in what is called the classic “breakfast, lunch, and dinner” pattern.
The EPA cautioned that the appearance of bites alone isn’t an accurate indicator of a bed bug infestation. Many times, these bites may be confused with rashes such as eczema or fungal infections. Sometimes, people who get bitten don’t seem to have a skin reaction at all.
Tips for getting rid of bed bugs
To date, there is no proof that bed bugs can transmit disease. However, you need to know how to eliminate these pests from your home.
- If you don’t want to use harmful chemicals, try something called “encasing.” This involves the use of bedding covers. You’ll need special sheets or padding to cover your mattress. This will trap bed bugs inside until they starve to death.
- When you’re at home, put all bedding and clothes in a hot dryer for about an hour. Washing alone won’t kill bed bugs, but hot, soapy water over 125 F could work. This strategy can also work on a backpack, which you need to wash once you return from a trip.
- Extreme cold can also kill bed bugs. For people who live in northern areas, four to five days of bedding exposure to temperatures near 0 F will kill the bugs.
- Use a vacuum on flooring and upholstery. Use a stiff brush to scrub mattress seams before vacuuming.
To get rid of bed bugs, you can also use natural remedies like diatomaceous earth, which is dusted over seams. If bed bugs travel over a lot of diatomaceous earth, their abdomen can tear, which will kill them in about two weeks. Use food-grade diatomaceous earth for this method, which isn’t recommended if you or someone in your home has lung issues like Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). Other options include tea tree oil or and rubbing alcohol.
You can read more articles about natural ways to get rid of bed bugs at Health.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: allergic reactions, allergies, bed bugs, C. lectularius, Cimex lectularius, cleanliness, common bed bug, health hazards, infestation, insects, parasites, pest control, pests, prevention, Public Health, skin infections