The medicinal potential of TCM herb, Gynura
01/31/2019 / By Ellaine Castillo
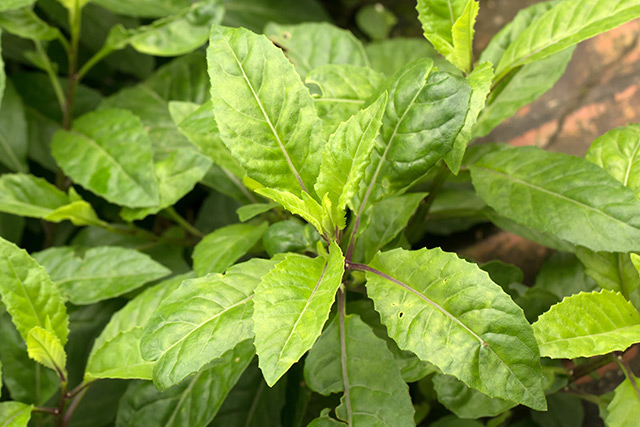

Researchers from Soochow University in China conducted a review on the different medicinal properties of Gynura (Gynura divaricata), a commonly used herb in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). Their findings, which were published in the African Journal of Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines, showed that Gynura contains compounds that contribute to its pharmacological properties.
- For centuries, TCM has been used to treat various diseases since it causes few side effects and has low toxicity. Studies have shown that TCM contains compounds with pharmacological activities like antioxidant, hypoglycemic, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer activity, which makes them extremely important for modern medicine.
- Gynura, also known as “Bai Bei San Qi”, is a widely used TCM herb for the treatment of respiratory problems, sore eyes, toothache, rheumatic arthralgia, and diabetes. Recently, it has also been approved as a new source of food in China.
- In this study, the researchers summarized the results of previous research on the chemical components and pharmacological properties of Gynura. To do this, they searched online journal databases for articles on the TCM herb between the years 1979 to 2016.
- Their search revealed that Gynura contains alkaloids, flavonoids, phenolic acids, terpenoids, polysaccharides, and aliphatic compounds.
- The team also found that Gynura has the ability to lower blood sugar and cholesterol levels, regulate blood pressure, neutralize free radicals, and prevent the growth and proliferation of cancer cells.
From these results, the researchers concluded that Gynura has a wide range of medicinal properties that can be attributed to the different phytochemicals that it contains.
The full text of the study is available at this link.
Read more news articles on different Traditional Chinese Medicines by visiting ChineseMedicine.news.
Journal Reference:
Xu B-Q, Zhang Y-Q. BIOACTIVE COMPONENTS OF GYNURA DIVARICATA AND ITS POTENTIAL USE IN HEALTH, FOOD AND MEDICINE?A MINI-REVIEW. African Journal of Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines. 2017;14(3). DOI: 10.21010/ajtcam.v14i3.12
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, anti-proliferative, antitumor, Gynura, Gynura divaricata, Herbs, natural remedies, plantmedicine, TCM, traditional Chinese medicine